Top 4 Qualities of a Diamond
Adjust the Importance to Fit Your Budget
Define Carat Weight
If someone has their eye (or heart) on a 1.5 carat diamond ring, a different carat size won’t often do. Just like some people want a compact car and others want a full-sized truck, the size of the diamond is a vital characteristic. However, one carat is equal to 100 points and a difference in even 1 point (.01 carats) can affect the cost of a diamond.
*Diamonds with equal carat weight may vary in value due to cut, color and clarity.
*Larger carat diamonds are more rare and a finished 1 carat diamond is truly one in one million.
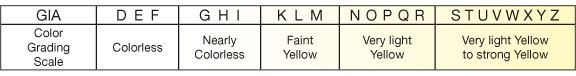
Decide on Color
Color, in this case, is actually lack of color in a white diamond. The color grade D is the purest white, or most colorless, diamond color. Diamonds graded D-J are near-colorless and Diamonds graded K-Z have increasing hues of yellow or canary.
You may not be able to distinguish the color of a diamond unless it is directly beside another diamond. Even then, slight differences in color may not be apparent unless compared on an all-white background.
* To decipher color, compare diamonds side-by-side on a pure white surface.
* The color of metal in a diamond ring setting can influence the appearance of a diamond's color.
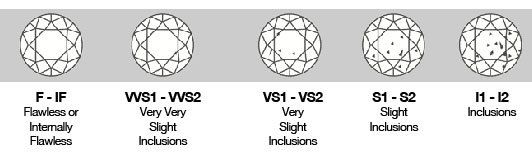
Choose a Clarity
Many people don’t notice the difference between similar grades of clarity, and diamonds graded as VS1 or VS2 have imperfections that are invisible to the naked eye. These diamonds are virtually flawless and the next step of SI1 and SI2 have slight inclusions that can appear more or less noticeable depending on the cut, color and carat. There are also natural colored diamonds and in this case more color intensity contributes to the rarity and value of a diamond.
* Diamonds are naturally formed in extreme heat and pressure deep in the earth. It is extremely rare to find a flawless diamond.
* The color and clarity can veil imperfections, which are identified under 10x magnification.
Select the Cut
Diamonds are the hardest natural material on earth and diamond cutting is a highly specialized craft. This extremely precise art is simply ranked as Excellent, Very Good, Fair and Poor. The facets of a diamond and the proportions of the angles cut transform the raw diamond into a brilliant spectrum of sparkle and color. Each cut and angle reduces the overall weight (carats) of the diamond so sometimes fire and brilliance is sacrificed for size.
* The scintillation (flicker of sparkle), fire (rainbow of color) and brilliance (bright white light) define the cut.
* The proportion of depth, width and table (top, flat cut) will influence the appearance of the size of the diamond.